- About
- Self-Directed IRA
- Sponsors Hub
- Assets
- Information Center
- Client Resources & Forms
- Contact Us
close
- About
- Self-Directed IRA
- Sponsors Hub
- Assets
- Information Center
- Client Resources & Forms
- Contact Us
close
A Self-Directed IRA is similar to a standard IRA. It's a retirement account that you contribute funds to, so that your retirement funds can grow through your investments. The difference between a standard IRA and a Self-Directed IRA is the types of investments your account can hold. A standard IRA allows you to invest in publicly-traded products like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. With a Self-Directed IRA, you can choose to invest in almost any type of alternative asset. It's common to use a Self-Directed IRA for investing in real estate, precious metals, and private placements.
A Self-Directed IRA (SDIRA) is an individual retirement account held by a custodian that allows you to invest in alternative assets such as real estate, private placements, promissory notes, and beyond.
Self-Directed IRAs give you, the investor, the power to diversify your portfolio, invest in what you know and believe in, and hedge against the stock market.
The fees for a Self-Directed IRA held at Madison Trust are among the lowest in the industry - and are set at a fixed rate regardless of the value in your account.
There are three simple steps to setting up a Self-Directed IRA: open an account, fund your account, and place your investment.
You may have heard the terms "self-directed retirement account," "alternative IRA," or "real estate IRA," but you could probably use some clarity. What exactly is a self-managed retirement account? What benefits does it have? And what possible effects can a Self-Directed IRA have as part of your retirement investment strategy?
Get answers from the Self-Directed IRA Specialists at Madison Trust, then you can feel confident to gain control of your retirement investments with a Self-Directed IRA.

If you're looking to start investing with a Self-Directed IRA, you're in the right place! We can help you learn:
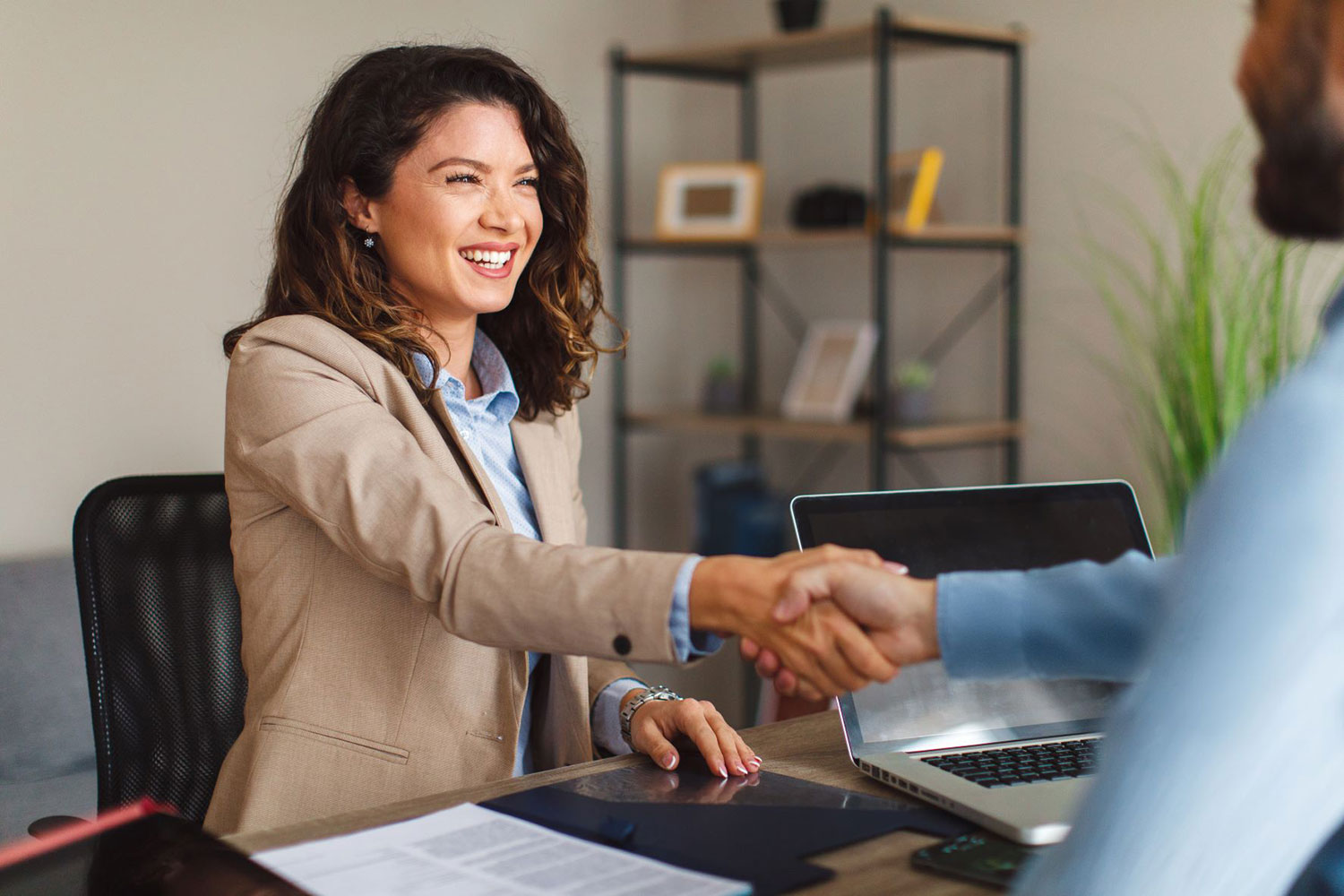

A Self-Directed IRA allows investors to diversify their retirement portfolios to include assets that are typically inaccessible in a standard IRA. With a Self-Directed IRA, you can invest in privately-held investments like real estate, private businesses, promissory notes, precious metals, and more, all within a tax-advantaged account.
Self-Directed retirement plans encourage individuals to invest in what they are familiar with. They provide investors with the power to put money into investments that make sense for them personally. Different people have different strengths and expertise, and it makes sense that their investments should reflect those strengths.
With a Self-Directed IRA, one can diversify beyond the volatility of the stock market and invest in products with a generally steadier, more reliable revenue stream. Popular alternative asset choices include rental properties, secured promissory notes, and tax liens.
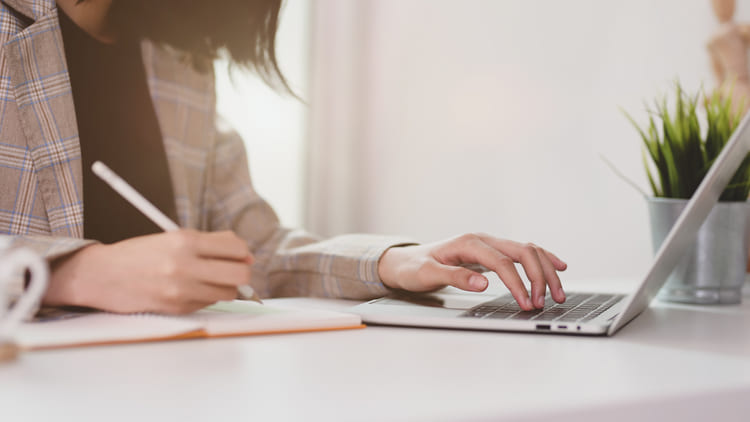

A Self-Directed IRA can legally invest in almost any asset. The only assets that are off-limits are collectibles, life insurance,
and S-Corporation stock. Some of the more popular investments include:
A Self-Directed IRA is an individual retirement account that allows you to invest in alternative assets beyond stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. You, as the account holder, direct your custodian to perform transactions on your behalf.
This type of Self-Directed IRA allows you, as the account holder, to perform your everyday transactions in real-time. This investing power is achieved through the creation of an entity, such as an IRA LLC or IRA Trust.
One concept that almost all investors and financial advisors can agree on is the importance of diversifying your portfolio. Investing in a variety of assets, including Wall Street products (stocks, bonds, and mutual funds) and alternative assets (real estate, precious metals, private placements, promissory notes, etc.) may reduce overall investment risk.
But you still may be wondering, "Which IRA is best for me?" Below are some of the basic differences between a standard IRA and a Self-Directed IRA.


Madison Trust is an industry-leading Self-Directed IRA custodian with a passion for empowering individuals to gain control of their retirement investing. Learn more about our story from our President & CEO, Daniel Gleich.

Among the lowest in the industry, Madison Trust offers competitive flat fees - set at a fixed rate regardless of the value of your account. For more information, visit our Fee Schedule.
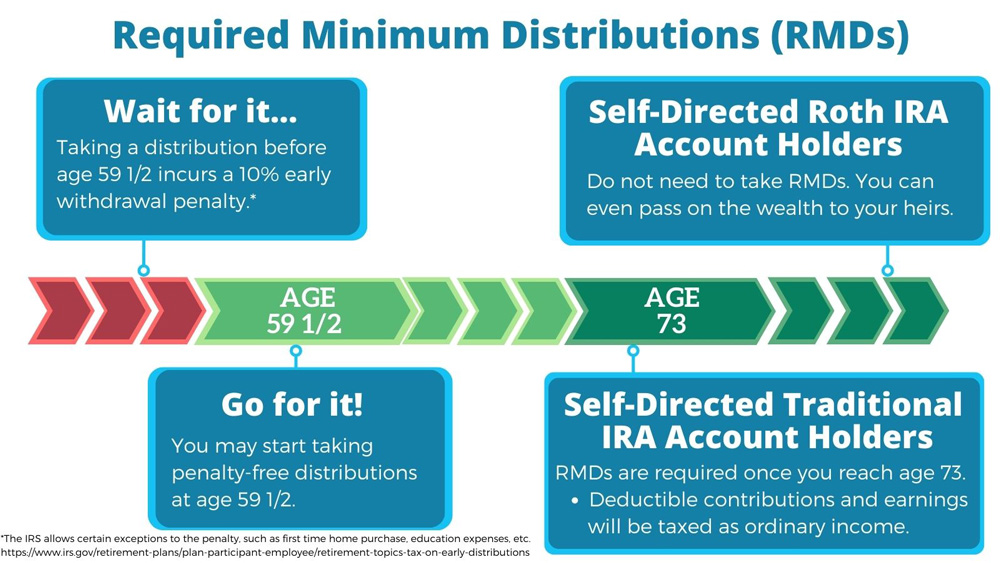
To start withdrawing funds from your Self-Directed IRA you must be at least age 59 ½. If you opened a Self-Directed Traditional IRA, you must take required minimum distributions (RMDs) each year after you turn age 73. Self-Directed Roth IRA account holders are exempt from taking RMDs, since taxes are paid upfront.
To receive funds earned through your Self-Directed Roth IRA investments without penalty, you must reach age 59 ½ and have the account opened for at least five years. Self-Directed Roth IRA contributions can be withdrawn at any time.
To learn more about distributions, visit Self-Directed IRA distribution rules.
At Madison Trust, we strive to make your Self-Directed IRA setup fast and simple. Once you fill out our easy online application, it typically takes about one to two weeks for your Self-Directed IRA to be funded.* Once your account is opened and funded, simply place an investment by instructing Madison Trust to send your funds directly to the investment of your choice.
*Please note, our processing timeframe does not include the transferring institution’s processing time. Turnaround time and delivery method back to Madison Trust is subject to the external institution’s processing times and procedures.
Yes, you can roll over your 401(k) into a Self-Directed IRA. You can rollover all – or a portion - of your funds. To do so, you will start the process by contacting your existing 401(k)’s plan administrator. For more information, view The Quick Guide to Funding a Self-Directed IRA with your 401(k).
When you invest with a Self-Directed IRA, all income from an investment returns directly back to the Self-Directed IRA without being taxed and without being added to your personal taxable income for that year. You can reinvest these earnings into another opportunity and keep growing your retirement savings in a tax-advantaged environment.
Like standard IRAs, potential tax benefits vary depending on your Self-Directed IRA account type. If you have a Self-Directed Traditional IRA, you can lower your income tax owed when you contribute to your account. If you have a Self-Directed Roth IRA, you pay taxes upfront, but you can take out your earnings tax-free in retirement.
Yes! All IRAs (including Self-Directed IRAs) must be held by a regulated custodian. A Self-Directed IRA custodian is responsible for administering the retirement account and holding custody of the IRA’s assets. Self-Directed IRA custodians allow account holders to invest beyond Wall Street and into alternative assets such as real estate, promissory notes, private placements, precious metals, and more. Visit The Guidelines on How To Choose the Right SDIRA Custodian.
Yes! Just like a standard IRA, anyone can open a Self-Directed IRA. To contribute to a Self-Directed IRA, the investor must earn taxable income. For more information, visit our blog Can Anyone Open a Self-Directed IRA?
The contribution limits for a Self-Directed IRA are the same as a standard IRA. If you are younger than 50 years old, you can contribute up to $7,000 in 2024 ($6,500 in 2023). If you are age 50+, you can contribute up to $8,000 in 2024 ($7,500 in 2023). Contributions for the year prior must be made by the tax filing deadline. For more information, visit Contributions FAQs.
In addition to annual contributions, you as the Self-Directed IRA account holder may also transfer or roll over all – of a portion of – your funds from an existing qualified retirement account such as an IRA or 401(k).
As a Self-Directed IRA account holder, you are not required to establish an LLC to invest in an alternative asset. Depending on your specific investments’ needs, establishing a Self-Directed IRA LLC may be beneficial. An IRA LLC enables you to invest your retirement money directly into the investment of your choice without having to contact your custodian for your everyday transactions. IRA LLCs are optimized for transaction-heavy investments, such as real estate rentals and fix-and-flips.
As a Self-Directed IRA account holder, you do not need to file an annual tax return. However, each year you must provide your Self-Directed IRA custodian with the fair market value (FMV) of your account. Visit IRS Tax Tips for Retirement Accounts for more information.
Your Self-Directed IRA would likely owe taxes if it generated business or trade income that is not related to the tax-exempt purpose of the IRA (Unrelated Business Income Tax) or when debt is leveraged to purchase an asset with your IRA (Unrelated Debt Financed Income).
A prohibited transaction is a transaction that involves the account holder or other disqualified persons benefiting from the IRA’s investments. A good rule of thumb is that an IRA may transact with third parties but may not transact with close family members or closely held entities.
To make a distribution from a Self-Directed IRA, complete a Distribution Request Form that details the distribution type, amount, and frequency of the distribution. If you are distributing an asset, please also submit a third-party certified value (i.e., an appraisal, letter from an investment sponsor, CPA-certified valuation, etc.). Depending on the asset, additional documents may also need to be submitted.
After the documents are submitted and approved, Madison Trust will send an Assignment of Interest to you. This documents the transfer of ownership from your IRA to your personal possession.



